14 5 As A Mixed Number
persisten
Dec 06, 2025 · 12 min read
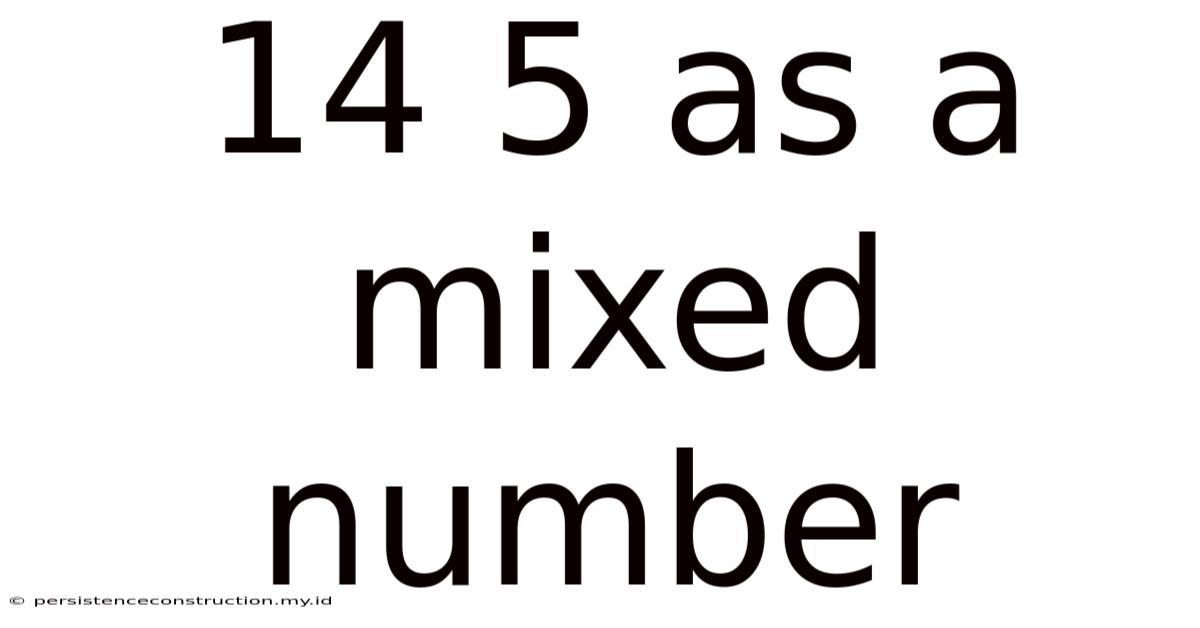
Table of Contents
Imagine you're baking a cake for a friend's birthday. The recipe calls for flour, and you realize you only have measuring cups that hold whole numbers. You need 14/5 cups of flour. How do you measure that out accurately using only whole cups and a fraction of a cup? This is where understanding how to convert improper fractions, like 14/5, into mixed numbers becomes incredibly useful.
The concept of converting improper fractions to mixed numbers isn't just a mathematical exercise; it’s a practical skill that helps us understand and work with quantities in everyday situations. From cooking and baking to carpentry and construction, the ability to express fractions in a way that's easy to visualize and measure is invaluable. Understanding 14/5 as a mixed number allows us to make sense of quantities that exceed a whole unit, presenting them in a format that’s easier to grasp and apply.
Understanding the Basics of Fractions and Mixed Numbers
To truly grasp the concept of transforming 14/5 into a mixed number, it’s important to first understand the basic building blocks: fractions, improper fractions, and mixed numbers. Each of these has its own unique characteristics and purpose in the world of mathematics.
A fraction represents a part of a whole. It consists of two main components: the numerator and the denominator. The numerator (the top number) indicates how many parts of the whole we have, while the denominator (the bottom number) indicates the total number of equal parts the whole is divided into. For example, in the fraction 1/4, the numerator '1' tells us we have one part, and the denominator '4' tells us the whole is divided into four equal parts.
There are different types of fractions, including proper fractions, improper fractions, and equivalent fractions. A proper fraction is one where the numerator is less than the denominator (e.g., 2/3). An improper fraction, on the other hand, is a fraction where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator (e.g., 5/3, 7/7). Improper fractions represent quantities that are one whole or greater than one whole. This leads us to the concept of mixed numbers.
A mixed number is a way to represent an improper fraction as a whole number and a proper fraction combined. It provides a more intuitive way to understand the quantity represented by an improper fraction. For instance, instead of saying 5/3, we can express it as the mixed number 1 2/3, which means one whole and two-thirds. Mixed numbers make it easier to visualize and conceptualize the amount being referred to, which is why they are commonly used in everyday contexts like cooking, measurement, and construction.
The Mathematical Foundation of Converting 14/5
The process of converting an improper fraction like 14/5 into a mixed number is rooted in the principles of division and remainders. The fraction 14/5 indicates that we are dividing 14 into 5 equal parts. However, since 14 is greater than 5, we know that we have more than one whole. To find out how many wholes we have and what fraction remains, we perform division.
The key idea is to divide the numerator (14) by the denominator (5). The quotient (the result of the division) represents the whole number part of the mixed number. The remainder represents the number of parts left over that are less than a whole. This remainder becomes the numerator of the fractional part, and the denominator remains the same as the original denominator.
In mathematical terms, the conversion process can be summarized as follows:
- Divide the numerator by the denominator: 14 ÷ 5 = 2 with a remainder of 4.
- Identify the whole number: The quotient, 2, is the whole number part of the mixed number.
- Determine the fractional part: The remainder, 4, becomes the numerator of the fractional part, and the denominator remains 5. So, the fractional part is 4/5.
- Combine the whole number and the fractional part: The mixed number is 2 4/5.
Therefore, 14/5 as a mixed number is 2 4/5. This means that 14/5 is equivalent to having two whole units and an additional four-fifths of another unit.
This method is consistent and can be applied to any improper fraction to convert it into a mixed number. The underlying principle is always to find out how many whole units are contained within the improper fraction and then express the remaining portion as a proper fraction.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Converting 14/5 into a Mixed Number
To make the conversion process even clearer, let's break it down into a detailed step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Understand the Improper Fraction Recognize that 14/5 is an improper fraction because the numerator (14) is greater than the denominator (5). This means the fraction represents a value greater than one whole.
Step 2: Perform Division Divide the numerator (14) by the denominator (5). 14 ÷ 5 = 2 with a remainder of 4.
Step 3: Identify the Whole Number The quotient from the division, which is 2, becomes the whole number part of the mixed number. This tells us that 14/5 contains two complete wholes.
Step 4: Determine the Fractional Part The remainder from the division, which is 4, becomes the numerator of the fractional part. The denominator of the fractional part remains the same as the original denominator, which is 5. Therefore, the fractional part is 4/5.
Step 5: Combine the Whole Number and Fractional Part Write the mixed number by combining the whole number (2) and the fractional part (4/5). So, 14/5 as a mixed number is 2 4/5.
Verification To ensure the conversion is correct, you can convert the mixed number back into an improper fraction:
- Multiply the whole number (2) by the denominator (5): 2 * 5 = 10.
- Add the numerator of the fractional part (4) to the result: 10 + 4 = 14.
- Place the result over the original denominator: 14/5.
Since the result matches the original improper fraction, the conversion is correct.
Practical Examples and Real-World Applications
Understanding how to convert improper fractions to mixed numbers isn't just an abstract mathematical concept; it has numerous practical applications in everyday life. Here are a few examples:
Cooking and Baking: Imagine you are following a recipe that calls for 7/3 cups of flour. Converting this improper fraction to a mixed number gives you 2 1/3 cups. This is much easier to measure out, as you can use two full cups and then add one-third of a cup.
Construction: Suppose you need 11/4 feet of lumber for a project. Converting this to a mixed number gives you 2 3/4 feet. This makes it easier to cut the lumber accurately, as you know you need two full feet and three-quarters of another foot.
Time Measurement: If an event lasts 5/2 hours, converting this to a mixed number gives you 2 1/2 hours, which is much easier to understand as two and a half hours.
Distance Measurement: If you need to walk 9/4 miles, converting this to a mixed number gives you 2 1/4 miles. This helps you visualize the distance as two full miles and a quarter of another mile.
In each of these examples, the conversion of the improper fraction to a mixed number provides a more intuitive and practical way to understand and apply the measurement or quantity.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While the process of converting improper fractions to mixed numbers is straightforward, there are some common mistakes that people often make. Being aware of these potential pitfalls can help you avoid them and ensure accuracy in your calculations.
One common mistake is incorrect division. Make sure you are dividing the numerator by the denominator correctly. A mistake here will lead to an incorrect whole number and remainder, resulting in the wrong mixed number.
Another mistake is forgetting the remainder. The remainder is crucial as it becomes the numerator of the fractional part. Forgetting the remainder or miscalculating it will lead to an incorrect fractional part.
A further mistake is changing the denominator. The denominator of the fractional part of the mixed number should always be the same as the denominator of the original improper fraction. Changing the denominator will result in an incorrect conversion.
Finally, not simplifying the fractional part of the mixed number can also be an oversight. If the fractional part can be simplified (e.g., 2/4 can be simplified to 1/2), it should be done to express the mixed number in its simplest form.
Tips for Mastering the Conversion Process
To master the conversion of improper fractions to mixed numbers, here are some helpful tips:
Practice Regularly: The more you practice, the more comfortable you will become with the process. Start with simple fractions and gradually work your way up to more complex ones.
Use Visual Aids: Visual aids like fraction bars or pie charts can help you visualize the fractions and understand the concept of converting improper fractions to mixed numbers.
Check Your Work: Always check your work by converting the mixed number back into an improper fraction to ensure you get the original fraction.
Simplify Fractions: Always simplify the fractional part of the mixed number to its lowest terms. This ensures that your answer is in the simplest form.
Understand the Concept: Don't just memorize the steps; understand the underlying concept of division and remainders. This will help you apply the process to different types of fractions.
Apply Real-World Examples: Use real-world examples to relate the concept to everyday situations. This will make the process more meaningful and easier to remember.
By following these tips, you can build a solid understanding of the conversion process and confidently convert any improper fraction into a mixed number.
Trends and Latest Developments
While the core concept of converting improper fractions to mixed numbers remains constant, there are some trends and developments in mathematics education that emphasize a more intuitive and practical approach to teaching this topic.
Emphasis on Visual Learning: Modern teaching methods often incorporate visual aids and hands-on activities to help students understand the concept of fractions. Tools like fraction bars, pie charts, and interactive simulations are used to make the learning process more engaging and effective.
Real-World Applications: Educators are increasingly focusing on real-world applications to demonstrate the relevance of fractions in everyday life. By using examples from cooking, construction, and measurement, students can see how fractions are used in practical situations.
Technology Integration: Technology plays a significant role in modern mathematics education. There are numerous apps and online resources that provide interactive exercises and tutorials on fractions. These tools can help students practice and reinforce their understanding of the topic.
Personalized Learning: Adaptive learning platforms can tailor the learning experience to each student's individual needs. These platforms can identify areas where a student is struggling and provide targeted instruction and practice.
Focus on Conceptual Understanding: Modern mathematics education emphasizes conceptual understanding over rote memorization. Students are encouraged to understand the "why" behind the mathematical procedures, rather than just memorizing the steps.
FAQ: Converting Improper Fractions to Mixed Numbers
Q: What is an improper fraction? A: An improper fraction is a fraction where the numerator (the top number) is greater than or equal to the denominator (the bottom number). Examples include 5/3, 7/4, and 10/10.
Q: What is a mixed number? A: A mixed number is a number consisting of a whole number and a proper fraction combined. Examples include 1 1/2, 2 3/4, and 5 1/3.
Q: Why do we convert improper fractions to mixed numbers? A: Converting improper fractions to mixed numbers makes it easier to understand and visualize the quantity represented by the fraction. Mixed numbers provide a more intuitive way to express values greater than one whole.
Q: How do I convert an improper fraction to a mixed number? A: To convert an improper fraction to a mixed number, divide the numerator by the denominator. The quotient becomes the whole number part of the mixed number, and the remainder becomes the numerator of the fractional part. The denominator remains the same.
Q: Can I convert a mixed number back to an improper fraction? A: Yes, to convert a mixed number back to an improper fraction, multiply the whole number by the denominator, add the numerator, and place the result over the original denominator.
Q: What if the remainder is zero when I divide the numerator by the denominator? A: If the remainder is zero, the improper fraction can be simplified to a whole number. For example, 6/3 simplifies to 2.
Q: Should I simplify the fractional part of the mixed number? A: Yes, always simplify the fractional part of the mixed number to its lowest terms. This ensures that your answer is in the simplest form.
Conclusion
Understanding how to express 14/5 as a mixed number is more than just a mathematical exercise; it’s a practical skill that enhances our ability to work with quantities in various real-world scenarios. By converting the improper fraction 14/5 into the mixed number 2 4/5, we gain a clearer understanding of its value, making it easier to apply in cooking, construction, and other everyday tasks.
Mastering the conversion process involves understanding the basic concepts of fractions, improper fractions, and mixed numbers, as well as following a step-by-step approach to division and remainder identification. Avoiding common mistakes and practicing regularly will further solidify your understanding.
Now that you have a comprehensive understanding of how to convert improper fractions to mixed numbers, put your knowledge to the test. Try converting other improper fractions into mixed numbers and see how this skill can simplify your daily tasks. Practice makes perfect, so keep honing your skills and enjoy the world of mathematics!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Greatest Common Factor Of 16 And 48
Dec 06, 2025
-
How Many Glasses Are In A Liter Of Water
Dec 06, 2025
-
Which Expression Represents The Volume Of The Prism
Dec 06, 2025
-
14 5 As A Mixed Number
Dec 06, 2025
-
How Many Feet In A Tenth Of A Mile
Dec 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 14 5 As A Mixed Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.